SPECTRUM
ALLOCATION IN THE 902-1240 MHz BAND
|
Frequency Band (MHz) |
Allocated Use |
FCC Rule Part |
|
|
|
|
|
902-928(1) |
Radiolocation/ISM |
ISM Equipment (18) |
|
|
|
Private Land Mobile (90) |
|
|
|
Amateur (97) |
|
|
|
|
|
928-932(2) (3) (4)
(5) |
Fixed |
Public |
|
|
|
Private Land Mobile (90) |
|
|
|
Fixed Microwave (101) |
|
|
|
Personal Communications (24) |
|
|
|
Fixed Microwave (101) |
|
|
|
|
|
932-935(2) (3) |
Fixed |
Fixed Microwave (101) |
|
|
|
Public |
|
|
|
|
|
935-940(2) (3) |
Fixed/Land |
Private Land Mobile (90) |
|
|
|
|
|
940-941(2) (3) (4) |
Fixed/Mobile |
Personal Communications (24) |
|
|
|
|
|
941-944(2) (3) (6) |
Fixed |
Public |
|
|
|
Fixed Microwave (101) |
|
|
|
|
|
944-960 |
Fixed |
Public |
|
|
|
Auxiliary Broadcast (74) |
|
|
|
Fixed Microwave (101) |
|
|
|
|
|
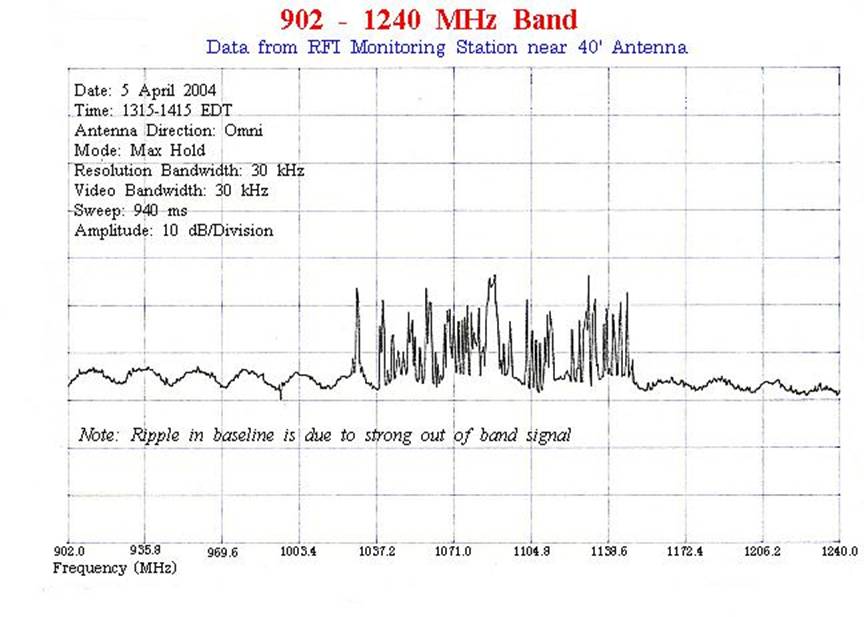
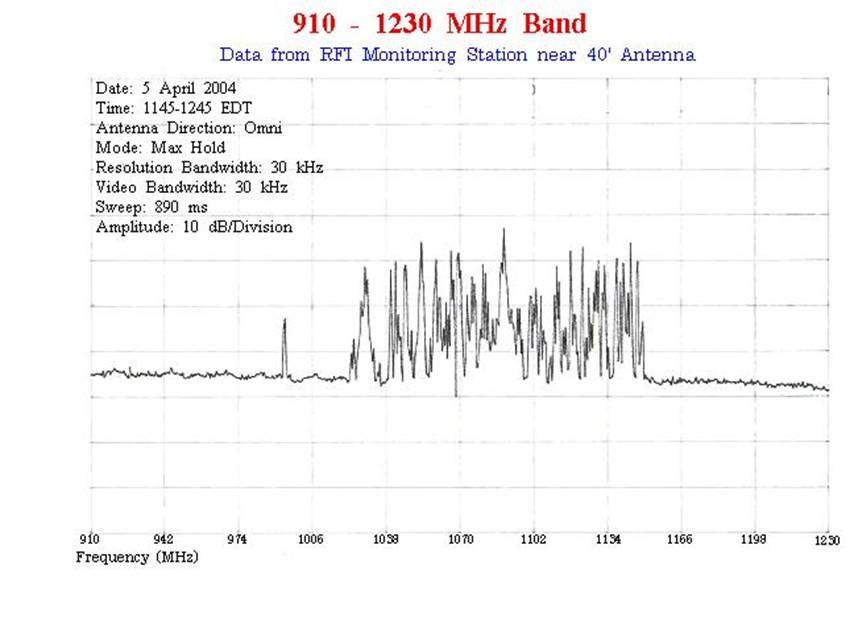
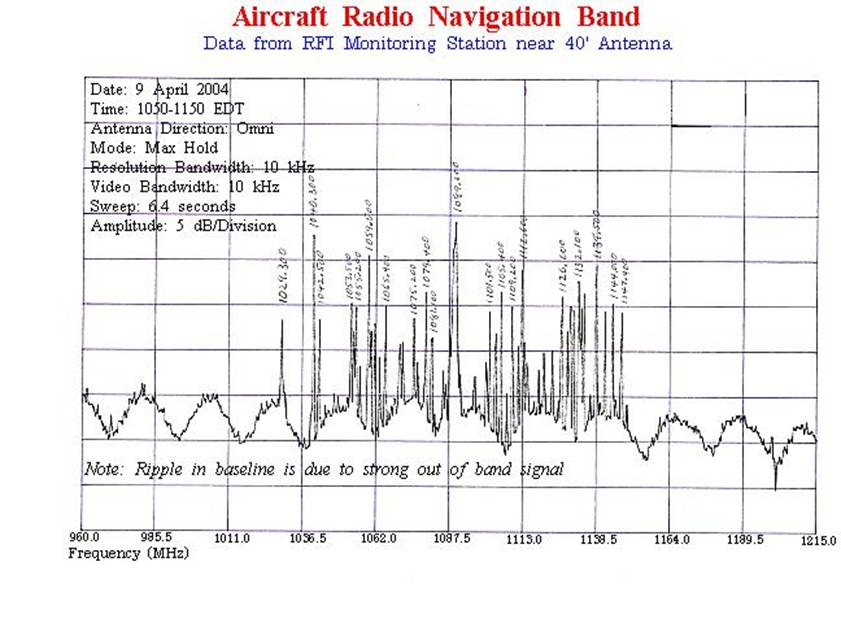
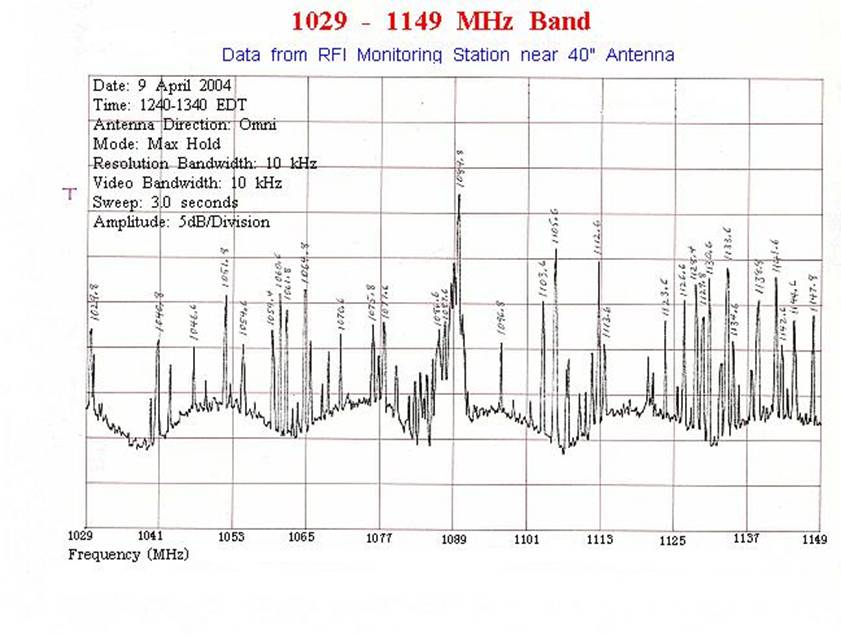
960-1215(7) |
Aeronautical Radionavigation |
Aviation (87) |
|
|
|
|
|
1215-1240(8) (9) |
Earth Exploration-Satellite (Active) |
|
|
|
Radiolocation |
|
|
|
Radionavigation-Satellite (Space-to- |
|
|
|
Space Research (Active) |
|
Footnotes
(1)The
band 902-928 MHz is available for Location and Monitoring Service (LMS) systems
subject to not causing harmful interference to the operation of all Government
stations authorized in these bands. These systems must tolerate interference
from the operation of industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) devices and the
operation of Government stations authorized in these bands. The band 902-928
MHz is allocated on a secondary basis to the amateur service subject to not
causing harmful interference to the operations of Government stations
authorized in this band or to Location and Monitoring Service (LMS) systems.
Stations in the Amateur service must tolerate any interference from the
operations of industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) devices, LMS systems,
and the operations of Government stations authorized in this band. Government
fixed and mobile radio services including low power radio control operations, are permitted in the band 902-928 MHz on a
secondary basis. In the band 902-928 MHz all Government non-military
radiolocation shall be secondary to military radiolocation.
(2)In the band 928-942 MHz, the Government radiolocation is limited
to the military services.
(3)Frequencies in the 928-960 MHz band may be assigned for multiple
address systems and mobile operations on a primary basis as specified in Part
94.
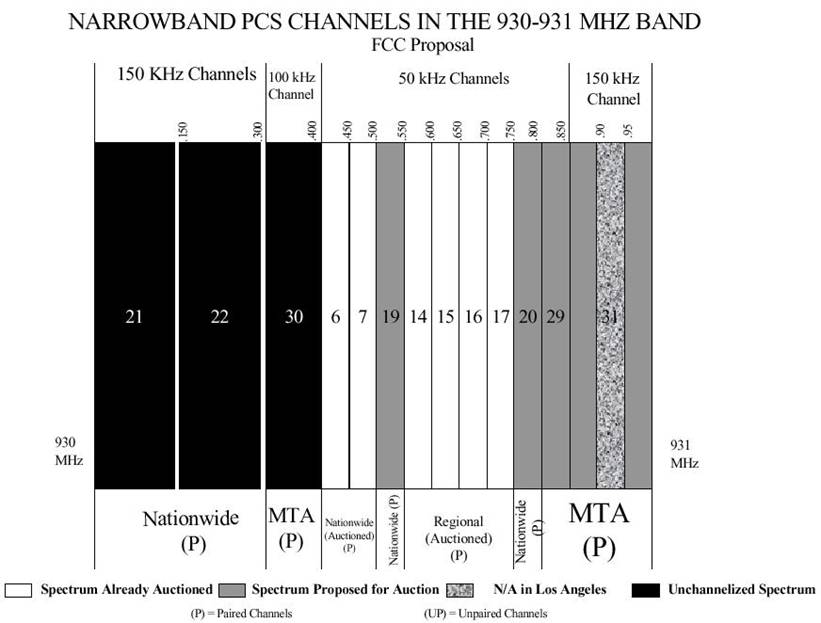
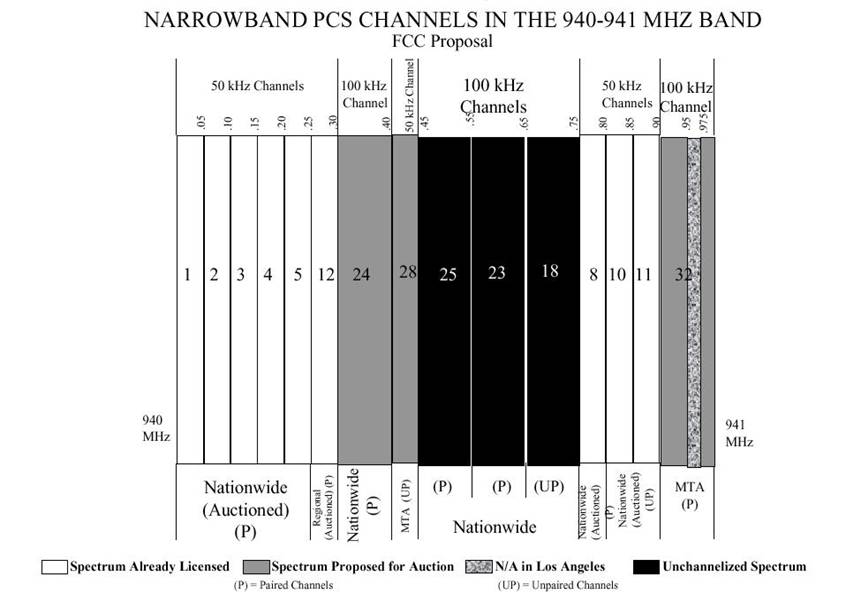
(4)Narrowband PCS operates in the 901-902 MHz, 930-931 MHz, and
940-941 MHz bands and is licensed based on nationwide, regional, and MTA market
designations. The rules governing narrowband PCS are found in the Code of
Federal Regulations, Volume 47, Part 24. Narrowband PCS is used to provide such
services as two-way paging and other text-based services. Licensees also use
the spectrum to offer wireless telemetry which is the monitoring of mobile or
fixed equipment in a remote location.
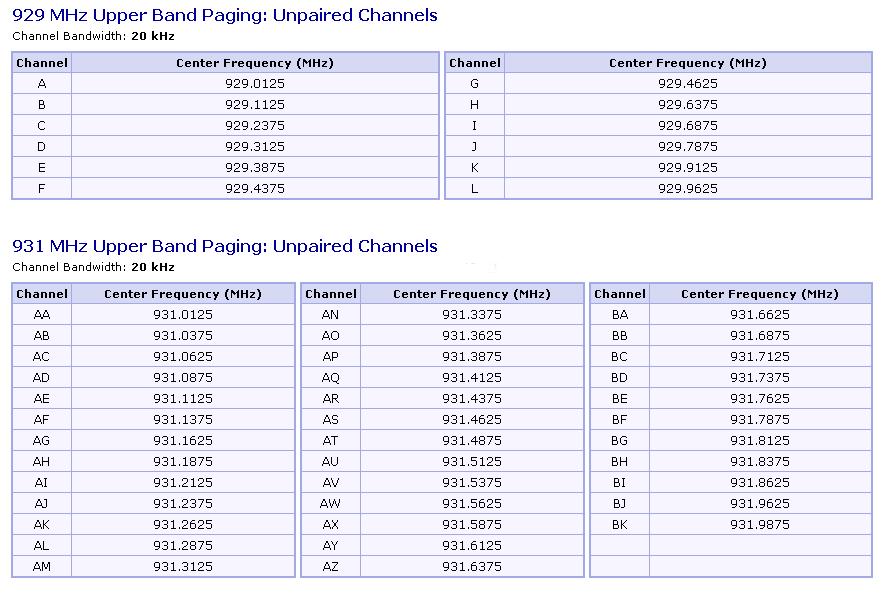
(5)Commercial paging may operate in the 929 and 931 MHz bands.
(6) The Channeling Plan for
assignments in this band is shown in Section 4.3.14 of the NTIA Manual.
(7) Government systems
utilizing spread spectrum techniques for terrestrial communication, navigation
and identification may be authorized to operate in the band 960-1215 MHz on the
condition that harmful interference will not be caused to the aeronautical radionavigation service. These systems will be handled on a
case-by-case basis. Such systems shall be subject to a review at the national
level for operational requirements and electromagnetic compatibility prior to
development, procurement or modification. For additional information on the use
of this band see: http://www.gb.nrao.edu/electronics/edir/edir313/dme_analysis.ps
(8)Government
radiolocation in the band 1215-1300 MHz is primarily for the military services;
however, limited secondary use is permitted by other Government agencies in
support of experimentation and research programs.
(9) The GPS satellites transmit on two L-band frequencies: L1 = 1575.42 MHz and L2 = 1227.6 MHz. Three pseudo-random noise (PRN) ranging codes are in use.
- The coarse/acquisition
(C/A) code has a 1.023 MHz chip rate, a period of 1 millisecond (ms)
and is used primarily to acquire the P-code.
- The precision (P) code has
a 10.23 MHz rate, a period of 7 days and is the principal navigation
ranging code.
- The Y-code is used in
place of the P-code whenever the anti-spoofing (A-S) mode of operation is
activated.
The C/A code is available on the L1 frequency and the P-code
is available on both L1 and L2. The various satellites all transmit on the same
frequencies, L1 and L2, but with individual code assignments.
Due to the spread spectrum
characteristic of the signals, the system provides a large margin of resistance
to interference. Each satellite transmits a navigation message containing its
orbital elements, clock behavior, system time and status messages. In addition,
an almanac is also provided which gives the approximate data for each active
satellite. This allows the user set to find all satellites once the first has
been acquired.
ADDITIONAL DATA
During GBT commissioning of the
Prime Focus receiver (PF2: 900-1240 MHz)
http://wwwlocal.gb.nrao.edu/~fghigo/rfi_pf1070/pf1070.html